Master C arrays Programming! This post dives into declaring & using arrays in C Programming, explains different array types, and equips you to manage data efficiently in your C programs. Level up your C skills today!

Arrays in C are like containers that hold multiple pieces of data. They’re handy for storing lots of information under one name. Here’s a quick overview:
- Declare an array: Tell the computer you want a container and how much stuff it should hold.
- Initialize: Put stuff into the container either when you create it or later on.
- Access: Get the stuff out of the container by giving each piece a number.
- Indexing: Think of it as finding stuff by its number in the container.
- Multi-dimensional: Sometimes you need containers inside containers for organizing lots of stuff.
- Passing to functions: Share the entire container with a function, not just one item.
- Operations: Arrays make sorting, searching, and other tasks easy.
- Best practices: Follow some rules to write better code with arrays.
- Advanced Techniques: Explore advanced concepts such as dynamic arrays, sparse arrays, or complex data structures built with arrays
- Array Interview Question and Answer
- Array 20 Top MCQ
Array in C Programming Language
An array is a variable which store more than one value same datatype in a continuous memory location. Array contain similar type of value. Array “index always begin with unique identification a[o]” is called index. Array index size always 0 to N-1.
In C, arrays are static data structures, meaning their size is fixed at compile time and cannot be changed during runtime. Each element in the array occupies a contiguous block of memory, and they are accessed using an index starting from zero.
Declare an array: C programming Language
Declaring an array in C is like telling the compiler to reserve a specific amount of memory for storing elements of a particular data type.
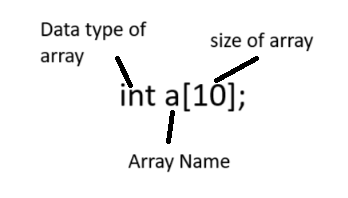
Syntax: datatype arrayName[arraySize];
Specifying Data Type: You define the type of data the elements in the array will hold. This could be integers (int), characters (char), floating-point numbers (float), or even custom data types.
Array Name: You choose a name to identify the array. This name will be used to refer to the entire collection of elements.
Size: You specify the number of elements the array can hold. This size must be a constant positive integer value.
Example: int a[5], int ch[6],char characters[10];
Access/ initialize Array C programming Language
Array Access (using index): Arrays store elements contiguously in memory. You use the array name and an index within square brackets [] to access specific elements.
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; initialize
printf(“Second element: %d\n”, numbers[1]); // Prints “Second element: 20” Access
array c programming examples Access, initialize, Declaration
int main() {
// Declaration and initialization of an array named "numbers" with values 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// Accessing and printing the third element of the "numbers" array
printf("Third element of the array: %d\n", numbers[2]); // Arrays in C are zero-indexed
// Changing the value of the fourth element of the "numbers" array
numbers[3] = 45;
// Printing all elements of the "numbers" array
printf("All elements of the array: ");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", numbers[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}Type of Array in C Programming Language
- One-dimensional array: This is the simplest form of an array where elements are arranged in a single row. Each element can be accessed using a single index.
- Multi-dimensional array: Arrays can have multiple dimensions, forming rows and columns. They are useful for representing tables, matrices, or grids of data.
One- Dimensional Array C
ne-dimensional arrays, also known as single-dimensional arrays, are fundamental building blocks in C programming. They provide a way to store a collection of elements of the same data type under a single name. Here’s a breakdown of key concepts:
You declare a one-dimensional array by specifying the data type, array name, and size enclosed in square brackets [].
ArrayDataType ArrayName[size]; example int stu[10];
Multi-dimensional array:
Multi-dimensional arrays are like one-dimensional arrays on steroids! They extend the concept of storing a collection of elements to a grid-like structure, allowing you to organize data in more than one dimension. Here’s a breakdown of key concepts:
You declare a multi-dimensional array by specifying the data type, array name, and size for each dimension within square brackets []
data_type array_name[size1][size2]…[sizeN];
Passing to functions Array
In C, when you pass an array to a function, you don’t actually pass the entire array itself. Instead, C passes arrays by reference. This means the function receives the memory address of the first element in the array. Here’s why this approach is taken:
- Efficiency: Passing a large array by value (copying all elements) would be time-consuming and memory-intensive. Passing the reference avoids this overhead.
- Modification: Functions can modify the elements of the original array since they’re working with the same memory location.
void function_name(data_type array_name[]);
array and string difference C Programming
Arrays and strings are both data structures used in C programming.
- Data Type:
- An array is a collection of elements of the same data type stored in contiguous memory locations.
- A string is a sequence of characters stored as an array of characters, terminated by a null character (
'\0').
- Termination:
- Arrays do not have any inherent termination mechanism. They are simply contiguous blocks of memory.
- Strings in C are terminated by a null character (
'\0'). This null character marks the end of the string and is used to indicate where the string ends.
- Initialization:
- Arrays can be initialized with a list of values at the time of declaration.
- Strings can be initialized using string literals enclosed in double quotes, which automatically include the null terminator.
- Functions:
- Arrays are manipulated using array-specific functions or by directly accessing individual elements.
- Strings have specialized functions in the C Standard Library (
<string.h>) for string manipulation, such asstrcpy(),strcat(),strlen(), etc.
- Null Termination:
- Arrays do not require null termination.
- Strings must be null-terminated to be recognized as strings in C.
Array MCQ question answer
array program in c for practice
Sum of Array Elements:
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
printf("Sum of array elements: %d\n", sum);
return 0;}
Largest Element in Array:
int main() {
int arr[] = {5, 2, 9, 10, 4};
int max = arr[0];
for(int i = 1; i < 5; i++) { if(arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
printf(“Largest element in array: %d\n”, max);
return 0;
}
Reverse an Array:
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int temp;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); // Size of array
for(int i = 0; i < n/2; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[n-i-1];
arr[n-i-1] = temp;
}
printf("Reversed array: ");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;}
Array Questions in C with solutions.
- What is an array in C?
- An array in C is a collection of elements of the same data type stored in contiguous memory locations.
- How do you declare an array in C?
- You declare an array in C by specifying the data type of its elements and the array’s size, like this:
int numbers[5];
- You declare an array in C by specifying the data type of its elements and the array’s size, like this:
- What is the index of the first element in an array?
- The index of the first element in an array is always 0.
- How do you access elements in an array?
- You access elements in an array using square brackets and the element’s index, like this:
numbers[2]to access the third element.
- You access elements in an array using square brackets and the element’s index, like this:
- What happens if you try to access an element beyond the array’s bounds?
- Accessing an element beyond the array’s bounds can result in undefined behavior, including program crashes or unexpected results.
- How do you initialize an array in C?
- You can initialize an array at the time of declaration by providing a comma-separated list of values enclosed in curly braces, like this:
int numbers[3] = {1, 2, 3};
- You can initialize an array at the time of declaration by providing a comma-separated list of values enclosed in curly braces, like this:
- Can you change the size of an array after it’s declared?
- No, the size of an array in C is fixed and cannot be changed after declaration.
- What is a multi-dimensional array?
- A multi-dimensional array in C is an array of arrays, allowing data to be organized in multiple dimensions, such as rows and columns.
- How do you pass an array to a function in C?
- You can pass an array to a function in C by specifying the array’s name as an argument. The function declaration should include the array’s data type and size (if known).
- Can you return an array from a function in C?
- No, C does not allow direct return of entire arrays from functions. However, you can return a pointer to an array or dynamically allocate memory within the function and return a pointer to it.
- What is the difference between static and dynamic arrays?
- Static arrays have a fixed size determined at compile time, while dynamic arrays can change in size during program execution using dynamic memory allocation functions like
malloc()andrealloc().
- Static arrays have a fixed size determined at compile time, while dynamic arrays can change in size during program execution using dynamic memory allocation functions like
- How do you find the length of an array in C?
- There is no built-in way to find the length of an array in C. You must keep track of the array’s size manually.
- What is the purpose of the sizeof operator in C?
- The sizeof operator in C is used to determine the size, in bytes, of a variable or data type. It can be used to find the size of an array by dividing the total size of the array by the size of its elements.
- How do you sort an array in C?
- You can sort an array in C using built-in sorting algorithms like bubble sort, selection sort, insertion sort, or by using library functions like
qsort().
- You can sort an array in C using built-in sorting algorithms like bubble sort, selection sort, insertion sort, or by using library functions like
- What is a null-terminated string in C?
- A null-terminated string in C is a character array that ends with a null character (
'\0'). It is used to represent strings in C programming.
- A null-terminated string in C is a character array that ends with a null character (
- How do you concatenate two arrays in C?
- You cannot concatenate arrays in C directly. Instead, you would typically create a new array large enough to hold the combined elements and copy the elements of both arrays into it.
- What is a jagged array?
- A jagged array is an array of arrays where each row can have a different number of elements. It is not directly supported in C, but can be simulated using arrays of pointers to arrays.
- How do you search for an element in an array in C?
- You can search for an element in an array in C using linear search or binary search algorithms, depending on whether the array is sorted or not.
- What is the difference between an array and a pointer in C?
- An array in C is a fixed-size collection of elements of the same data type, while a pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable or data structure.
- How do you dynamically allocate memory for an array in C?
- You can dynamically allocate memory for an array in C using functions like
malloc()orcalloc(). For example,int *arr = (int*)malloc(5 * sizeof(int));allocates memory for an integer array of size 5.
- You can dynamically allocate memory for an array in C using functions like
C Programming Quiz & MCQ
1.Part-1 C MCQs | C mcq questions and answers | Top 50 MCQs in C
2 .Master the C basics: 50 essential C MCQs with solutions
3. Challenge Yourself: Basic C Programming MCQ Quiz: Test Your Fundamentals (For beginners)
4. C Output for Beginners: Predicting Output with Confidence
5. Debugging C Output: A Guide to Understanding and Predicting Program Output
6. Basics of C Programming MCQ Boost Your Skills with Targeted Questions ( introduction C Programming)
7. Integer Array in C – How to Declare Int Arrays with C Programming (freecodecamp.org)
1 thought on “All About Array C Programming Language: Programming Hack 2024”